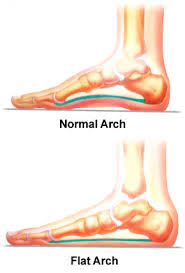
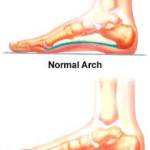
 Pes Planus or Flat Foot is a decreased medial longitudinal arch and a pronated hind foot (aka “flat foot”).
Pes Planus or Flat Foot is a decreased medial longitudinal arch and a pronated hind foot (aka “flat foot”).
Causes of Flat Feet:
- hyper mobility
- poor biomechanics of subtler joint and metatarsal joint
- shortened gastrocs, soleus, or Achilles
- weakness in tibialis posterior
- congenital bony abnormalities in foot
- congenital bony abnormalities in leg and thigh
- poor posture
- nerve lesions causing paralysis or muscle weakness
- trauma
- poor footwear flat feet massage flat foot massage for flat feet
Flat Feet Massage: SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
- hypermobility of medial arch and pronated foot
- pain may be present in plantar surface, usually with overuse and fatigue
- short peroneus longus, peroneus brevis, peroneus tertius, gastrocnemius, and soleus muscles
- lengthened and weak tibialis posterior, tibialis anterior, long toe flexors, and intrinsic muscles of the foot
- other conditions present (plantar fasciitis, shin splints, and iliotibial band contracture)
Flat Feet Massage: CONTRAINDICATIONS
- mobilizing hypermobile joints is contraindicated
- do not stretch tibialis anterior and posterior. Allows increased pronation of foot
- avoid heat on plantar surface when fasciitis is present
- friction massage technique when client is on anti-inflammatory medication is contraindicated
Flat Feet Massage: ASSESSMENT
OBSERVATION:
- pronation occurs throughout entire gait cycle
- mild pes planus: 4-6 degrees hind foot valgus
- moderate pes planus: 6-10 degrees hind foot valgus
- severe pes planus: 10-15+ degrees hind foot valgus
- Achilles tendon= valgus
- internal tibial torsion possible
- valgus at knees
- internal rotation at hip possible
- medial arch is flat; foot pronated
- talar head bulges medially. Redness or callus where shoe rubs talar head
- valgus at first metatarsal joint
- forefoot abduction
- mortons foot
- Second metatarsal longer than the first
PALPATION:
- tenderness at spring ligament, navicular, calcaneus attachment of the long plantar ligament and plantar fascia, first and second metatarsal head and first metatarsophalangeal joint.
- heat local to first metatarsophalangeal joint with bunions and on plantar surface if plantar fasciitis is present
- thick, rough texture of skin over talar head and the first and second metatarsal heads
- hypertonic and lengthened intrinsic foot muscles, tibialis anterior, tibialis posterior, and long toe flexors
- shortened and hypertonic gastrocs, soleus, peroneus longus, peroneus brevis, and peroneus tertius
- trigger points present in peroneus longus and brevis
ROM:
Active Free:
- Eversion in non-weight bearing calcaneus greater than 10 degrees
- Dorsiflexion of ankle limited with severe pes planus
- Increased internal rotation with femoral ante version
Passive Relaxed:
- Tarsal joints and other joints of medial longitudinal arch are hypermobile
- Plantarflexion and dorsiflexion reduced with restricted ankle joint capsule
- Pain when passive eversion of calcaneus, supination of the foot and extension of toes with low grade inflammation of ligaments or plantar fascia
- Hypomobility in pronated superior tibiofibular joint
- Increased internal rotation of hip with femoral anterversion
- External rotation of hip decreased
Active Resisted:
- Reduced strength of tibialis anterior, tibialis posterior, and extensor hallucis longus
SPECIAL / ORTHOPEDIC TESTING:
- test for structural or functional Pes Planus
- morton’s neuroma
Flat Feet Massage: Treatment Goals
- decrease SNS firing, fascial restrictions, pain, HT, TP’s, adhesions
- massage compensating structures
- treat other conditions, if any
- stretch shortened muscles
- increase circulation, esp. to weak, taut structures
- mobilize hypomobile joints
Flat Feet Massage Therapy Treatment:
PRONE:
- gastrocs/soleus:
- MFR, DMS, Effleurage, Petrissage
- . Stretch (+peroneals)
- foot: Repetitive effleurage
SUPINE:
- joint play tibiofibular joint/ankle
- Use Stimulating Techniques: Tibialis anterior/posterior, Toe flexors intrinsic foot muscles (medial arch)
- Passive Stretch: gastrocs/soleus and peroneals
- Circulatory massage techniques to the whole leg
Flat Feet Massage: Homecare
hydrotherapy:
- contrast foot baths after prolonged stress
- apply ice local to inflammation
strengthen:
- tibialis anterior/posterior
- intrinsic foot muscles
stretch:
- gastrocs/soleus
- peroneus longus, brevis, and tertius
other:
- avoid activities that stress medial longitudinal arch
- arch support
- self massage leg, foot, and ankle